Tesla’s workforce has long been a barometer for its scale, ambition, and operational challenges. Dramatic shifts in headcount reflect both external pressures and internal restructuring. In the auto, energy, and AI sectors, changes in Tesla’s staffing ripple across supply chains, investor models, and labor markets. In electric vehicle production, for instance, plant expansions in Texas or Shanghai depend directly on labor availability; in software and AI, Tesla’s ability to retain engineers determines its competitive edge over peers like Waymo or Rivian. Read on to see detailed trends, distributions, and productivity metrics shaping how many people work at Tesla today.
How Many People Work at Tesla?
- Tesla employed 125,665 people worldwide as of December 31, 2024, down from 140,473 the prior year.
- That decline represents a –10.54% year-over-year reduction in headcount.
- In 2023, Tesla’s headcount had grown to 140,473, a ~9.87% increase over 2022.
- Revenue per employee in 2024 is estimated at ~ $777,380, up from ~$688,910 in 2023.
- Tesla’s productivity metric (revenue per employee) places it among the more efficient automakers.
- The workforce reduction in 2024 equated to a cut of about 14,808 employees.
- In 2024, Tesla executed layoffs of over 10% of its workforce, following an April announcement to reduce redundancies.
Recent Developments
- In April 2024, Elon Musk announced a plan to reduce staff by ~10% globally to cut costs and eliminate redundant roles.
- Those cuts translated to about 14,000+ roles eliminated across various departments.
- Following the layoffs, Tesla’s headcount fell from 140,473 in 2023 to 125,665 in 2024.
- In early 2025, Tesla moved to acquire parts of German firm Manz AG, absorbing over 300 jobs at a Reutlingen site.
- Tesla also shuttered or restructured its internal Dojo supercomputer team, shifting some AI work to external vendors.
- Some software, service, and engineering teams faced further cuts just months after the main layoffs.
- Tesla’s global expansion continues, with new operational demands in regions like the Middle East (e.g., Cybertruck rollout in Qatar) that may necessitate further staffing in localized markets.
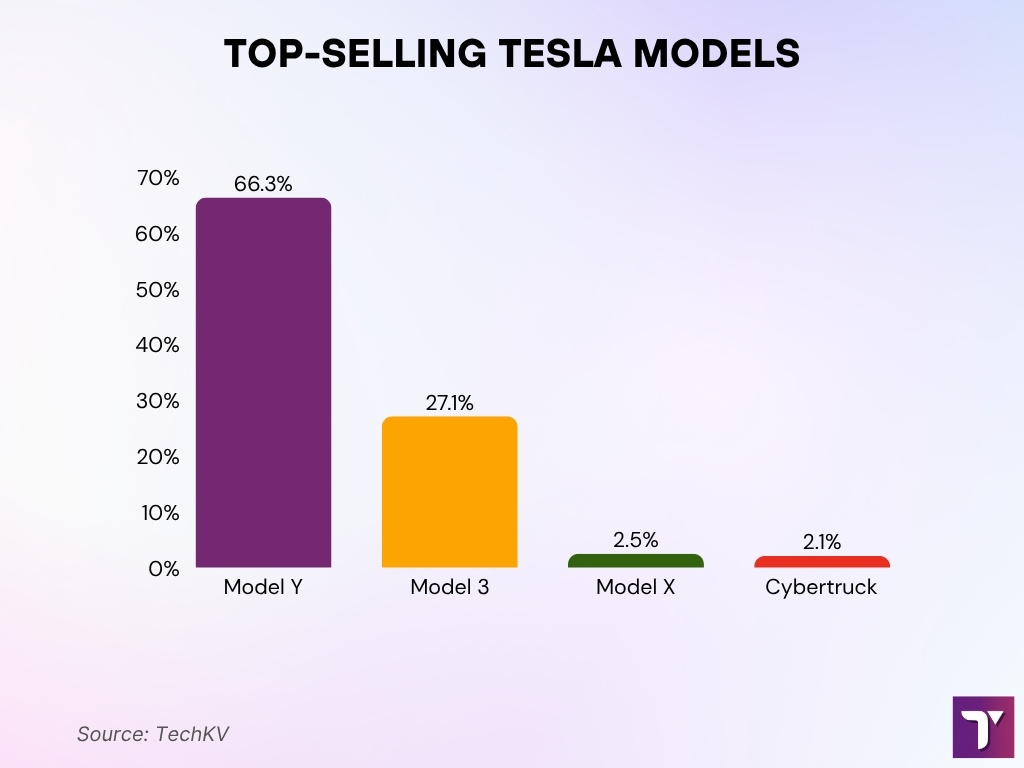
Best-Selling Tesla Models
- Model Y dominates with 1,185,757 units sold, representing 66.3% of Tesla’s total sales.
- Model 3 ranks second with 484,026 units sold, making up 27.1% of sales.
- Model X accounts for 2.5% of total units sold, reflecting its niche luxury market.
- Cybertruck holds 2.1%, showing early but growing adoption in its launch phase.
Tesla’s Current Team (Key People)
- Elon Musk remains Tesla’s CEO and Product Architect, focusing on strategic initiatives like Full Self-Driving, Dojo AI training, and the Cybertruck program.
- Vaibhav Taneja serves as Chief Financial Officer (CFO) and oversees all financial, accounting, and investor relations functions.
- Tom Zhu is SVP of Automotive, managing global vehicle production and Gigafactory operations. Previously, he led Tesla China and played a key role in Gigafactory Shanghai.
- Andrew Baglino, formerly SVP of Powertrain and Energy Engineering, resigned in early 2024 after 18 years at Tesla. His departure left a leadership gap in energy R&D.
- Lars Moravy continues to lead Vehicle Engineering, responsible for structural and mechanical engineering across Tesla’s entire vehicle lineup.
- Rebecca Tinucci, Senior Director of the Supercharger business, exited in 2024 as part of restructuring, leading to changes in Tesla’s EV charging strategy.
- Ashok Elluswamy, Director of Autopilot Software, leads Tesla’s AI and autonomy engineering team. He played a pivotal role in the development of Full Self-Driving Beta and Dojo.
- Rohan Patel, VP of Public Policy and Business Development, resigned in 2024 during organizational streamlining.
- Tesla’s Board of Directors includes Robyn Denholm (Chair), Ira Ehrenpreis, Kathleen Wilson-Thompson, Joe Gebbia, and JB Straubel, Tesla’s former CTO and now CEO of battery recycler Redwood Materials.
Total Number of Tesla Employees
- As of December 31, 2024: 125,665 employees globally.
- The 2024 count reflects a net reduction of 14,808 employees from the prior year.
- That decline corresponds to a 10.54% decrease in staff from 2023 to 2024.
- In 2023, Tesla reported 140,473 employees.
- The 2023 figure represented nearly +9.87% growth over 2022.
- In 2022, Tesla had 127,855 employees.
- Earlier, in 2021, Tesla employed 99,290 people, which then ballooned into later growth periods.
- The 2024 drop marks the first major contraction after years of headcount expansion.
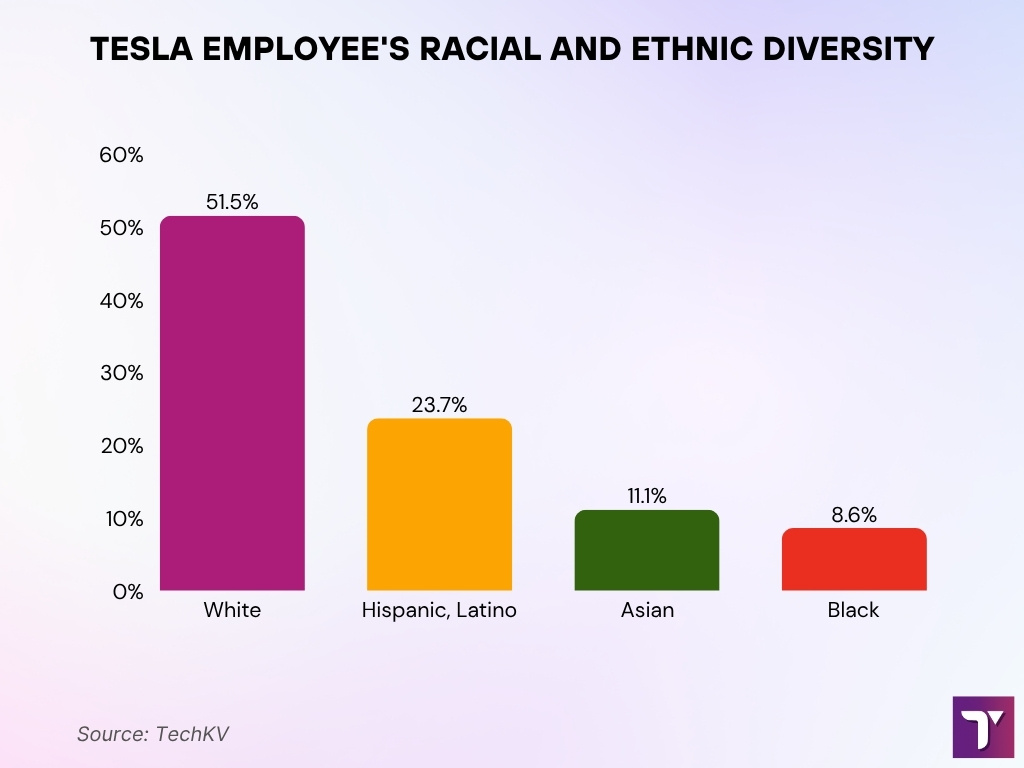
Tesla Employee Demographics and Diversity (U.S. & UK)
- 51.5% of Tesla’s U.S. workforce is White. Hispanic or Latino workers make up 23.7%, followed by 11.1% Asian and 8.6% Black or African American employees.
- Women represent about 21–22% of Tesla’s U.S. workforce. Despite modest overall representation, women hold roughly 17% of director and VP roles.
- Tesla’s U.S. leadership is predominantly male at around 83%. About 59% of leaders identify as White.
- Asian employees hold roughly 25% of senior management roles. That’s higher than their 21% share of the total workforce.
- In the UK, Tesla’s 2023 gender pay report shows women earn slightly more on average. Mean base pay for women is 2.6% higher, though median pay is 1.1% lower than men’s.
Headcount by Year
- 2024: 125,665 employees (–10.54% vs 2023).
- 2023: 140,473 employees (+9.87% vs 2022).
- 2022: 127,855 employees (+28.77% vs 2021).
- 2021: 99,290 employees (+40.33% vs 2020).
- 2020: 70,757 employees.
- 2019: 48,016 employees.
- 2018: 48,817 employees (a slight rise).
- Pre‑2018: Growth was more constrained, e.g., 2017 at 37,543, 2016 at 17,782, 2015 at 13,058.
Tesla’s Global Workforce Distribution
- Tesla operates major manufacturing facilities in the United States, China (Shanghai), Germany (Berlin/Brandenburg), among others.
- In China, Gigafactory Shanghai is a central node; as of mid‑2023, it was reported to employ ~20,000.
- In Texas, Gigafactory Texas has scale ambitions and in prior media was expected to employ tens of thousands, adjustments in 2024–2025 trimmed ~12% at one point.
- Regional splits (U.S., China, Europe) shift year to year based on capacity, demand, and cost pressures (though Tesla does not publicly publish precise headcount by country).
- Tesla emphasizes vertical integration across energy, battery, and software roles, which merges R&D and production in many geographies.
- Some acquisitions (e.g., Manz in Germany) bring ~300 employees into Tesla’s European base.
- Workforce skews toward manufacturing in Asia and the U.S., while software and energy staff are more globally dispersed across smaller offices and R&D centers.
- Tesla’s Supercharger network spans regions, support, deployment, and maintenance roles exist in North America, Europe, Asia‑Pacific, corresponding to station counts.
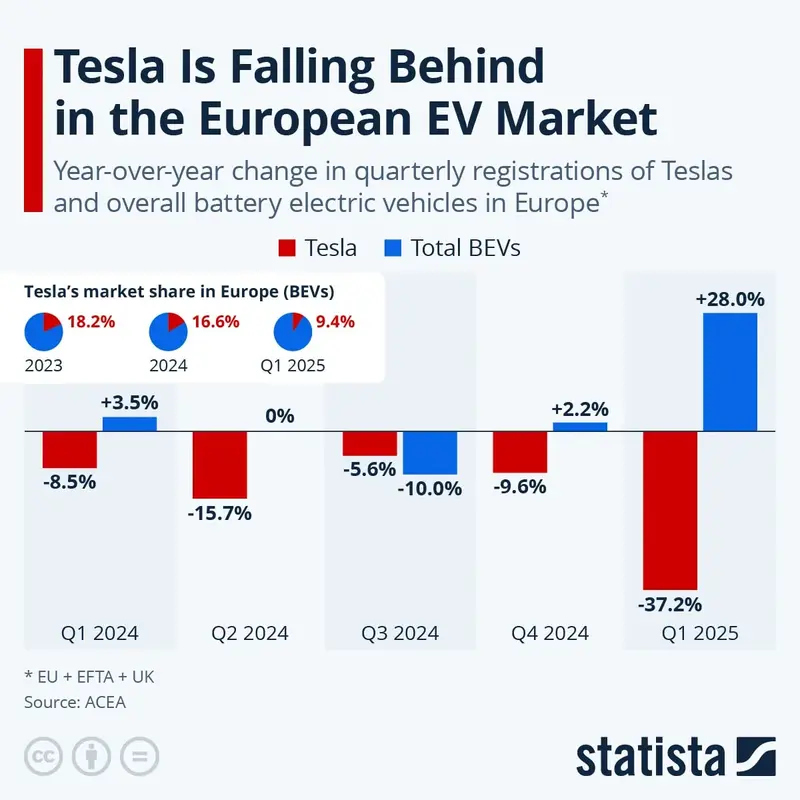
Tesla’s Declining Performance in the European EV Market
- Tesla’s market share in Europe fell from 18.2% in 2023 to 16.6% in 2024, then to 9.4% in Q1 2025. This marks a significant year-over-year decline in regional dominance.
- In Q1 2024, Tesla registrations dropped by 8.5%. Meanwhile, the overall BEV market grew by 3.5%.
- In Q2 2024, Tesla declined 15.7% in registrations. The total BEV market remained flat at 0% growth.
- In Q3 2024, Tesla slipped 5.6% year-over-year. However, the overall BEV market declined even more at 10.0%.
- In Q4 2024, Tesla registrations dropped 9.6%. The broader BEV market still grew by 2.2% in contrast.
- By Q1 2025, Tesla saw a massive 37.2% plunge in sales. The rest of the BEV market surged 28.0% during the same period.
Employees by Location
- The Fremont, California, factory employs about 22,000 people as of recent reports.
- Gigafactory Berlin‑Brandenburg reports ~ 11,500 workers.
- Gigafactory Shanghai had ~ 20,000 employees in mid‑2023.
- Texas (Austin / Gigafactory Texas / corporate HQ region) saw its headcount drop ~7% in 2024, settling at 21,191 employees in the metro area.
- Tesla’s Buffalo, New York, solar / technology sites laid off 285 employees in 2024, about 14% of that site’s ~ 2,032 staff.
- Tesla operates ~ 1,350 retail, service, delivery, and body shop locations globally.
- The company’s global footprint spans the U.S., China, Germany, and other markets, but Tesla does not publicly disclose full country‑level headcounts for many regions.
- As operations shift (e.g., localizing supply chains), location shares may change faster than annual reports reflect.
Tesla Employees by Department
- Engineering is Tesla’s largest discipline, with ~ 17,810 employees (≈40% of total).
- Operations / Manufacturing / Supply Chain roles number ~ 8,120 employees.
- Sales & Support / Customer‑facing functions employ ~ 5,225 people.
- Business Management / Strategy teams number ~ 4,853 employees.
- Finance & Administration departments account for ~ 1,961 employees.
- IT (Information Technology) staff are ~ 1,520.
- Human Resources comprises about 1,422 workers.
- Additional departments, Marketing & Product (~1,165), Consulting (~1,331), and “Other” (~2,512), cover cross‑functional and support roles.
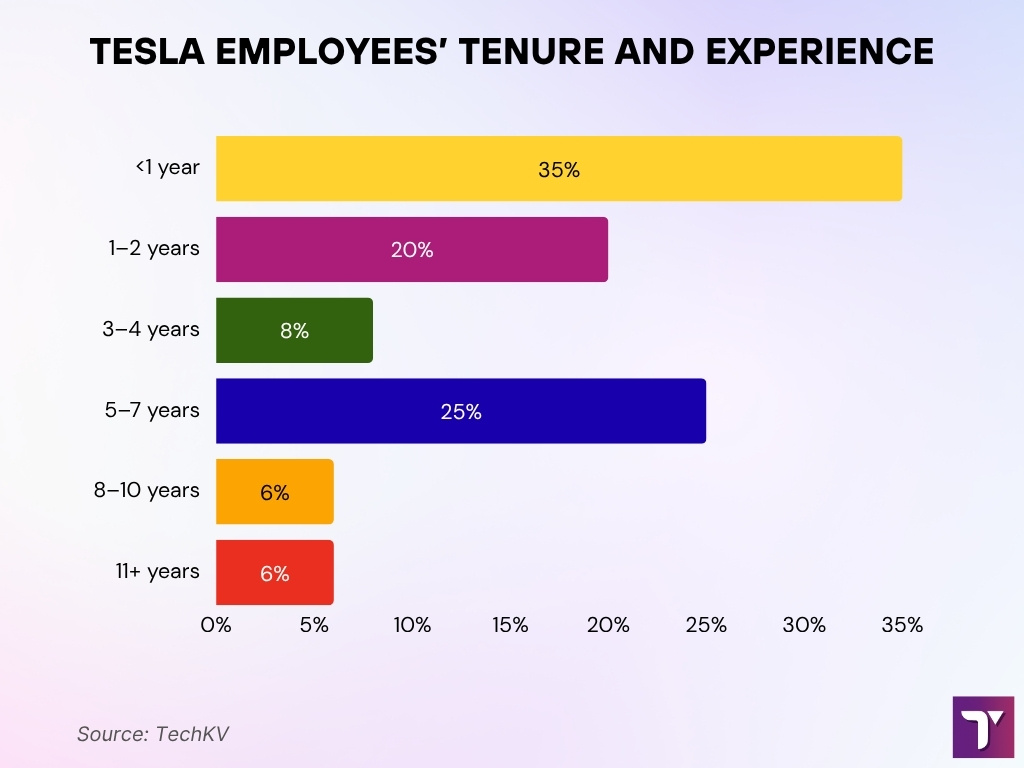
Tesla Employee Tenure and Experience Breakdown
- The average employee tenure at Tesla is 3.7 years. This reflects moderate retention across a rapidly scaling workforce.
- Roughly 35% of Tesla employees stay less than 1 year. This is the largest single tenure group, indicating high early attrition.
- About 20% of employees remain for 1 to 2 years. This shows a sizable portion exists within the early career phase.
- Only 8% of employees stay for 3 to 4 years. This group represents a smaller, mid-tenure segment.
- 25% of employees stay between 5 to 7 years. This is Tesla’s second-largest tenure bracket and indicates growing long-term retention.
- Around 6% of workers have been with Tesla for 8 to 10 years. These employees likely joined during the company’s early growth stages.
- Another 6% have stayed for over 11 years. This small but stable group includes many early veterans and leadership roles.
Operations and Manufacturing Staff
- The combined “Operations / Manufacturing” bucket (including supply chain) is ~ 8,120 employees.
- The Fremont factory alone has ~ 22,000 employees (some overlap with operations) across vehicle assembly, testing, and related functions.
- Gigafactory Berlin hosts ~ 11,500 workers focused on battery, powertrain, and vehicle assembly tasks.
- Gigafactory Shanghai, with ~ 20,000 employees, is central to Tesla’s Asia production.
- Some plants reduce staffing, for example, Berlin reduced shift intensity in 2023, affecting employment levels.
- Tesla uses contract and temporary workers in many manufacturing roles (not always counted in employee totals).
- Operational headcount is sensitive to production volume; periods of ramp‑up or slowdowns lead to fluctuating factory staffing.
- In restructuring rounds in 2024, some cuts targeted factory support roles, supply chain, and tooling operations.
Workforce Reduction and Layoffs
- In April 2024, Tesla announced ~10% global staff reductions, affecting ~14,000 roles.
- The reduction from 2023 to 2024 saw a drop from 140,473 to 125,665 employees (–10.54%).
- Some software and service teams were hit in later waves, beyond the initial cut.
- Buffalo, NY operations cut ~14% (285 employees).
- Texas (Travis County / Austin area) saw layoffs of ~2,688 roles in factory & HQ areas.
- In Tesla’s 2024 SEC filing, ~ $583 million in employee termination expenses was recognized as a restructuring cost.
- These workforce cuts mark the first major contraction following years of headcount expansion.
- Tesla’s restructuring plan emphasized eliminating redundant roles rather than across‑the‑board cuts.
- The layoffs triggered ripple effects in vendor, supplier, and gig‑worker networks tied to Tesla’s operations.
Employee Demographics
- Tesla’s workforce is ~ 22.5% female and ~ 77.5% male.
- Racial/ethnic composition: ~ 35.7% White, 26.6% Hispanic/Latino, 19.6% Asian, 10.8% Black/African American, and 7.3% other.
- As of December 31, 2024, U.S. employees who are veterans / active-duty = 2.3%.
- Employees identifying as individuals with disabilities = 3.3%.
- Those who are veterans with disabilities = 1.2%.
- Management tenure: ~ 68% of managers promoted internally (from non‑manager roles).
- ~ 45% of the management team has been at Tesla for over five years.
Gender Distribution of Tesla Employees
- ~ 22.5% of Tesla’s workforce is female.
- ~ 77.5% are male.
- In engineering and technical fields, female representation is often lower than the company average.
- Female representation in leadership roles (VPs, directors) is lower than the company average.
- Comparatively, many tech and manufacturing firms aim for ~30–35% female presence, so Tesla lags in that benchmark.
- Periodic diversity reports suggest Tesla is increasing female hiring in non-engineering divisions.
- As Tesla ramps AI, software, and service functions, female share in those departments might trend upward.
Educational Background of Tesla Employees
- Over 78% of Tesla employees have at least a bachelor’s degree.
- Approximately 19% of the workforce holds a master’s degree.
- Less than 1.5% hold PhDs.
- Popular alma maters include Stanford University, MIT, University of Michigan, and UC Berkeley.
- Engineering, computer science, and mechanical engineering are among the most common majors.
- Tesla also hires graduates from trade schools and vocational training programs.
- In-house programs like the Tesla START program offer technical training in EV systems.
- Tesla regularly recruits from top engineering competitions like Formula SAE and Hyperloop Pod Challenge.
- A significant number of employees also come from online course backgrounds.
H‑1B Visa Employees and Trends
- In FY 2024, Tesla filed 724 H‑1B visa applications.
- This was down from 1,180 filings in FY 2023.
- Over 70% of Tesla’s H‑1B petitions are for engineering and software-related roles.
- Common job titles include Software Engineer, Mechanical Engineer, Data Scientist, and Battery Engineer.
- The average salary for Tesla H‑1B employees in 2024 was $124,900.
- Most visa holders are based in California, Texas, and Nevada.
- Tesla also sponsors green cards (PERM applications) for long-term foreign workers.
- H‑1B approvals at Tesla have a success rate of over 94%.
- Tesla continues to advocate for expanding high-skill visa quotas.
Revenue and Profit Per Employee
- In 2024, Tesla’s revenue per employee was approximately $777,380.
- Tesla’s net income per employee in 2024 was approximately $56,740, according to the company’s annual net income of ~$7.13 billion divided by 125,665 employees.
- Compared to GM, Tesla remains more productive per capita.
- Year-over-year, revenue per employee increased by 12.8%.
- Operational efficiencies at Gigafactories contributed to better output per employee.
- Tesla’s gross profit margin was around 18.2%.
- Tesla’s revenue per employee ranks it among the top 5 global automakers in efficiency.
- R&D-heavy divisions yield the highest output per worker.
Market Capitalization Per Employee
- Tesla’s market capitalization in early 2025 was approximately $586 billion.
- That translates to $4.66 million in market cap per employee.
- This figure fell slightly from 2023’s ~$5.2 million per employee.
- Apple’s market cap per employee: ~$7.9 million.
- Nvidia’s: ~$25 million.
- GM’s: ~$400K.
- In 2020, Tesla’s market cap per employee was just ~$1.9 million.
- The 2024 workforce reductions actually increased per-employee ratios slightly.
- The figure is especially important given Tesla’s lower margins compared to software companies.
Comparison With Previous Years
- 2021: 99,290 employees.
- 2022: 127,855 employees (+28.77% YoY).
- 2023: 140,473 employees (+9.87% YoY).
- 2024: 125,665 employees (–10.54% YoY).
- Tesla’s workforce contracted for the first time in over a decade in 2024.
- From 2012 to 2022, Tesla averaged annual employee growth of 30–35%.
- 2024’s cutbacks were primarily attributed to overexpansion and margin pressure.
- Despite headcount drops, revenue per employee rose.
- Tesla has added over 112,000 employees since 2015.
- Employee attrition remained higher in 2024, but many layoffs were strategic.
- Future headcount trends depend on factors like Cybertruck adoption, Full Self-Driving progress, and global policy shifts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Tesla is listed with 125.67 K employees in sources like Macroaxis, aligning closely with its 2024 disclosed figures.
Tesla’s net income per employee in 2024 was approximately $56,740, down 46.86% from 2023.
Tesla’s revenue per employee was about $777,380, a 12.84% increase from 2023.
Tesla reported 125,665 employees as of December 31, 2024.
Conclusion
Tesla’s workforce reflects both the scale of its ambitions and the constraints of today’s EV landscape. While headcount shrank for the first time in years, dropping to 125,665 employees, the company continues to generate more revenue per employee than nearly every traditional automaker. This blend of contraction and operational efficiency suggests a maturing business that’s moving from hypergrowth to strategic optimization.
However, challenges remain. Gender diversity lags industry benchmarks, and layoffs in AI and engineering could hamper long-term innovation. Still, Tesla’s ability to maintain high productivity metrics and a strong global footprint keeps it at the center of the EV and AI convergence.
For stakeholders tracking Tesla’s human capital, the data tells a story of shifting strategy, tightened operations, and continuing relevance in a turbulent tech-manufacturing economy.
