AI in healthcare is accelerating transformation, from diagnosing illnesses faster to streamlining hospital workflows. Impact spans advanced diagnostics to drug development and patient documentation. For example, AI is cutting drug development timelines by over 50% in some cases, and ambient‑AI scribes are already easing burnout for clinicians. Explore the stats that reveal just how fast change is unfolding.
Editor’s Choice
- The global AI healthcare market grew from $29 billion in 2024 to $39 billion in 2025, a 44% CAGR forecast to hit $504 billion by 2032.
- Another report tags 2024’s size at $26.6 billion, rising to $36.7 billion in 2025, aiming for $187.7 billion by 2030 at ~38.6% CAGR.
- As of 2025, 86% of U.S. health organizations report using some form of AI, though most use remains administrative.
- A national survey shows 66% of physicians now use AI in practice (up from 38% in 2023), and 68% see definite or some advantage in AI tools.
- 85% of U.S. healthcare leaders were exploring or had adopted generative AI by late 2024.
- Over 340 FDA‑approved AI tools, especially in radiology, are now in clinical use. Two‑thirds of U.S. radiology departments employ AI.
- More than 1 in 3 Americans (35%) use AI for health and wellness tasks such as symptom research or emotional support.
Recent Developments
- AI cuts drug development costs and timelines by over 50%; Recursion moved a cancer candidate to trials in 18 months versus the 42‑month average.
- Abridge, an ambient‑AI scribe startup, doubled its valuation to $5.3 billion and is used in 150+ U.S. health systems, projected to assist in 50 million clinical conversations in 2025.
- Healthcare startups like Sword Health and Hinge Health are using AI to increase patient load per provider (Sword: from 200–300 to 700) and reduce clinician time in therapy by 95%.
- Despite predictions of replacement, AI in radiology complements rather than replaces specialists, over 340 FDA‑approved tools are deployed, assisting in cancer and stroke detection, and two‑thirds of U.S. radiology departments use AI today.
- AI could extend coverage to the 4.5 billion people currently lacking essential healthcare access.
- The U.S. introduced 59 AI‑related federal regulations in 2024, more than twice the number from 2023.
Global AI Healthcare Market Size
- Valued at $29.01 billion (2024), the market is projected to grow to $39.25 billion (2025) and $504.17 billion by 2032, a 44% CAGR.
- Another estimate shows $26.57 billion in 2024, growing to $36.67 billion in 2025, and heading to $187.69 billion by 2030 at a 38.6% CAGR.
- $21.66 billion by the end of 2025, growing from $14.92 billion in 2024 at a 38.6% CAGR toward $110.61 billion by 2030.
- From $1.1 billion in 2016 to $22.4 billion in 2023, reaching $32.3 billion in 2024, with 40% projected growth by 2025.
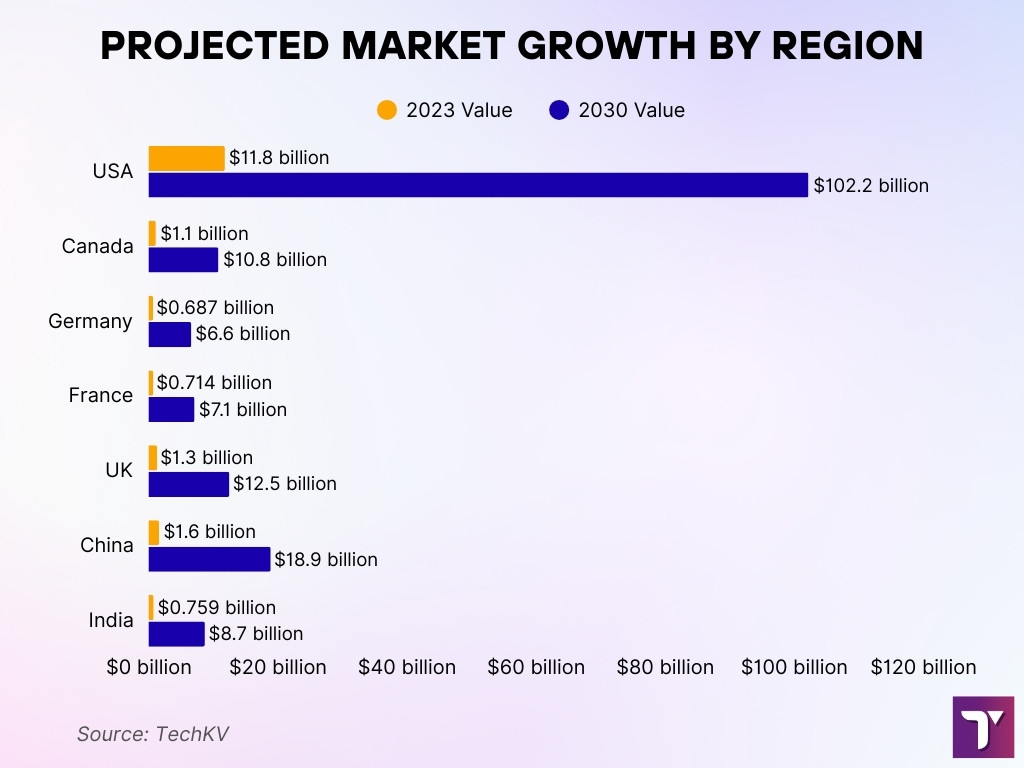
- The U.S. AI healthcare market is forecast to surge from $11.8 billion (2023) to $102.2 billion by 2030, a 36.1% growth rate.
- North America commanded 49.3% of the global AI healthcare market in 2024.
- Software solutions held over 46% of the revenue share in 2024 in AI healthcare.
Regional AI Market Statistics
- North America accounted for nearly 49–54% of the global AI healthcare market in 2024.
- U.S.-specific AI healthcare market: $12.01 billion+ in 2024.
- Projected growth ratios by region (2023 to 2030):
- USA: $11.8 billion to $102.2 billion (+36.1%).
- Canada: $1.1 billion to $10.8 billion (+37.9%).
- Germany: $0.687 billion to $6.6 billion(+38.2%).
- France: $0.714 billion to $7.1 billion (+38.8%).
- UK: $1.3 billion to $12.5 billion(+37.8%).
- China: $1.6 billion to $18.9 billion (+42.5%).
- India: $0.759 billion to $8.7 billion(+41.8%).
AI Adoption in Healthcare
- 86% of U.S. health orgs used AI as of late 2024, mostly in back-office or admin functions.
- 66% of physicians already use AI in practice (2024), up from 38% in 2023, and 68% see clear benefits.
- Generative AI adoption: 85% of healthcare leaders explored or adopted it by the end of 2024.
- 60% of clinicians report AI helps uncover health patterns and diagnoses beyond human detection, and 86% overall leverage AI.
- Radiology: Two‑thirds of radiology departments use AI, and 340+ FDA‑approved tools support imaging diagnostics.
- Public adoption: 35% of Americans use AI for health management tasks.
- Generative AI leadership: U.S. private AI investment reached $109.1 billion in 2024, with $33.9 billion for generative AI, up 18.7% from 2023.
AI Applications in Healthcare
- In drug development, AI can cut costs and timelines by over 50%, accelerating trials. Recursion achieved 18‑month progress to phase 1 versus the industry’s 42‑month average.
- Ambient‑AI scribes (e.g., Abridge) help capture 50 million doctor‑patient conversations in 2025, reducing documentation time.
- Startups like Sword Health use AI to raise patient caseloads per provider from 200–300 to 700, and Hinge Health saves 95% of clinician time with AI tools.
- Radiology uses over 340 AI‑approved tools for detecting tumors, strokes, and more. Adoption in U.S. departments is at 66%.
- AI can bridge healthcare for 4.5 billion people without essential services.
- Generative AI is making inroads swiftly; 85% of healthcare leaders are exploring or adopting capabilities.
- Around 60% of clinicians believe AI reveals patterns that human providers miss.
- U.S. private AI investment hit $109.1 billion in 2024, with $33.9 billion in generative AI.
Generative AI in Healthcare
- The generative AI healthcare market is valued at $2.9–3.3 billion in 2025, expected to approach $ 40 billion by 2035, with a 28–32% CAGR.
- 46% of U.S. health organizations are already in the early stages of Gen‑AI adoption, and 70% of payers and providers are actively pursuing implementation.
- 83% of healthcare organizations are piloting generative AI, but fewer than 10% have invested in enterprise‑wide infrastructure.
- Among organizations implementing Gen‑AI, 61% plan to partner with vendors, 20% aim to build in‑house, 19% will buy off‑the‑shelf solutions.
- In 2024, generative AI attracted $33.9 billion in global private investment, up 18.7% over 2023.
- 78% of organizations used AI in 2024, up from 55% in 2023.
- 40% of U.S. physicians are ready to use generative AI in point‑of‑care patient interactions.
AI in Imaging and Diagnostics
- The global AI in medical imaging market was $1.36 billion in 2024, poised to reach $19.78 billion by 2033, at a 34.7% CAGR.
- Another forecast notes $1.67 billion in 2025, rising to $14.46 billion by 2034, at a 27.1% CAGR.
- The global AI in diagnostics market is expected to spike from $ 7.03 billion in 2025 to $ 96.52 billion by 2032, a 45.4% CAGR.
- AI tools in imaging achieve accuracy levels above 95% for conditions like lung cancer and retinal disorders.
- AI-driven cancer diagnostics now match expert tumor board decisions in 93% of cases.
- An AI stroke‑diagnostic software tripled full recovery rates from 16% to 48%, by diagnosing over an hour faster.
- An AI‑powered stethoscope diagnoses heart failure twice as accurately, atrial fibrillation three times, and valve disease nearly twice as often within 15 seconds.
- AI-enhanced imaging is transforming workflows with tools that combine multiple imaging modalities and clinical data for richer insights.
AI in Medical Imaging Market: Key Statistics and Forecast
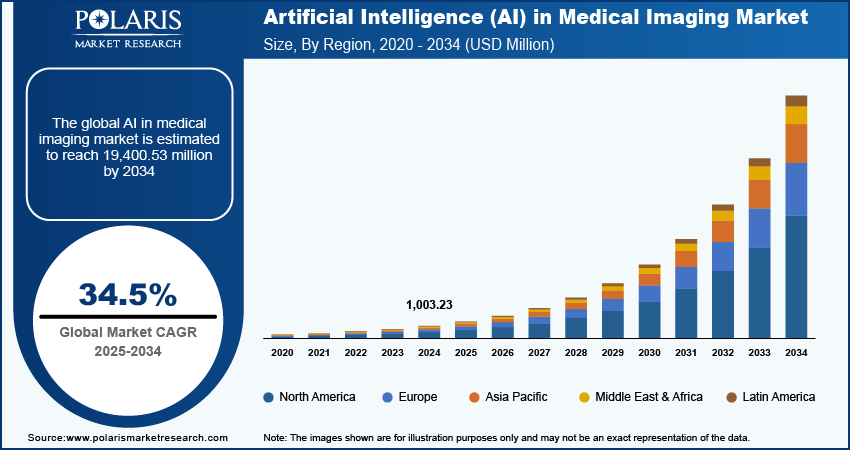
- The global AI in medical imaging market is projected to reach $19,400.53 million by 2034.
- The market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 34.5% from 2025 to 2034.
- In 2025, the market size is forecasted to cross $1,003.23 million, marking a significant acceleration from previous years.
- The growth is driven by increasing adoption of AI in diagnostics, rising demand for early disease detection, and integration with imaging systems.
- North America leads the market share, followed closely by Europe and the Asia Pacific, based on stacked bar chart trends in the forecast period.
- The Asia Pacific region shows the fastest growth rate among all, reflecting increased AI investments in countries like China, Japan, and India.
- Middle East & Africa and Latin America represent smaller shares but are projected to grow steadily through 2034.
- Annual growth appears exponential, especially post-2025, indicating accelerated adoption of AI tools in radiology and diagnostics.
- Key contributors to this growth include AI advancements in CT, MRI, and X-ray technologies, along with automated image interpretation.
Treatment and Drug Discovery
- AI can slash drug development costs and timelines by over 50%, with companies moving candidates to trials in 18 months vs. 42 months.
- By 2025, 30% of new drugs are estimated to be discovered using AI, cutting up to 40% time and 30% cost in early stages.
- AI-discovered drugs reach Phase I trials with 80–90% success, compared to 40–65% for traditional methods.
- The AI in the drug discovery market was $1.72 billion in 2024, forecast to reach $ 8.53 billion by 2030, at a 30.6% CAGR.
- Fewer than 24% of AI companies apply AI beyond target discovery and design into later preclinical development.
- Alphabet’s Isomorphic Labs raised $ 600 million to accelerate AI-driven drug design using AlphaFold-based technology.
- AMD invested $20 million in Absci Corp, signaling increased competition in biologics acceleration via AI.
Patient Monitoring and Outcomes
- By 2025, approximately 71 million Americans (26%) will use some form of remote patient monitoring (RPM).
- RPM usage spans specialties: 29% internal medicine, 21% cardiology, 19% family practice.
- AI-powered RPM enables real-time health deterioration detection, personalized interventions, and wider access to care.
- AI tools assist doctors with fracture detection, patient triage, and early disease signs, aiding care for 4.5 billion people globally.
- AI decision tools are becoming mainstream in 2025, providing clinicians with instant access to evidence and minimizing diagnostic errors.
- Advanced AI systems integrate imaging with data to improve predictions on disease progression and treatment response.
- Only 19% of institutions report high success using AI for clinical diagnosis, indicating a need for better clinician-AI collaboration.
Hospital and Healthcare Management
- The smart hospital market, powered by AI, IoT, and robotics, may grow to $148 billion by 2029.
- Use cases include sepsis risk prediction, voice-controlled interfaces, equipment tracking via RFID, and robot-supported surgeries.
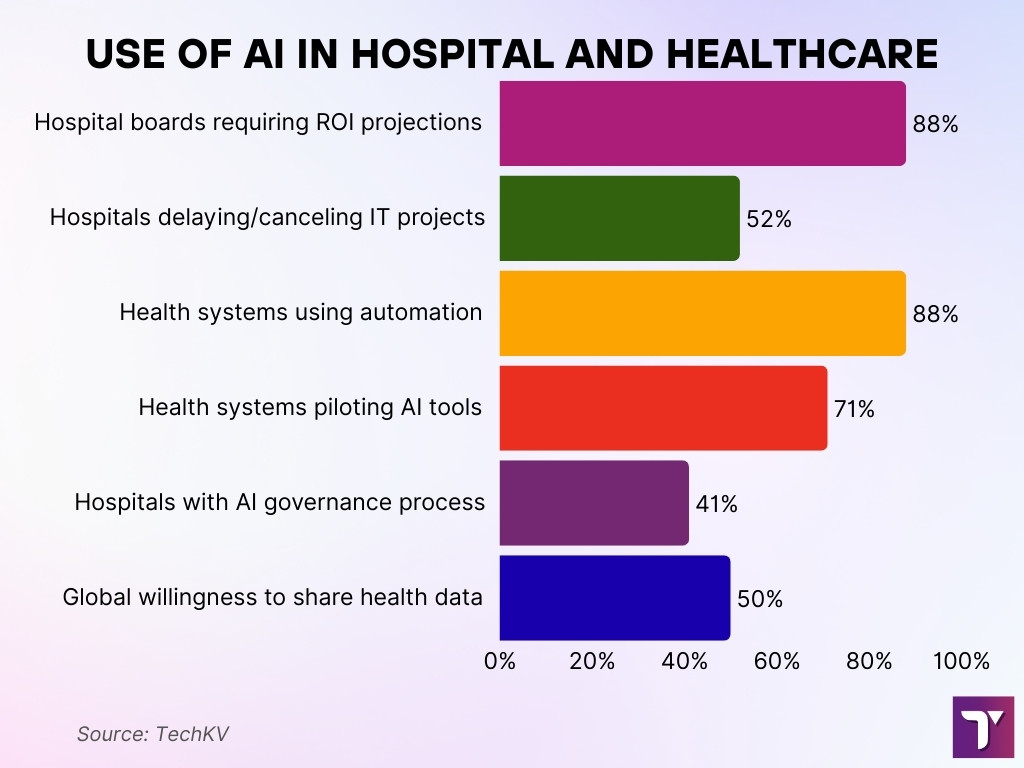
- In 2025, 88% of hospital boards required ROI projections for IT projects, and 52% of U.S. hospitals delayed or canceled projects with long payback timelines.
- Radiology AI delivered up to a 791% ROI when radiologist time savings were calculated.
- 88% of health systems use some automation, 71% pilot AI tools, but only 36% have fully deployed AI solutions.
- 70% have some AI governance process, up from 41% in 2024, though formal data policies remain limited.
- AI helps streamline revenue cycle management, reducing costs in an industry that spends $440 billion annually on administration.
Return on Investment for AI in Healthcare
- Radiology AI systems demonstrated an ROI of 7.9:1, mainly by saving specialist time and improving reporting speed.
- In billing, AI-led coding accuracy improved by 25–35%, while claims denials dropped by 15–18%, speeding revenue cycles.
- AI-enabled virtual assistants handling patient queries and intake reduce front-desk loads by 40–60%.
- Generative AI used in clinical documentation can save 4–6 hours weekly per physician, lowering burnout and attrition costs.
- AI helps reduce avoidable hospital admissions by 19%, particularly in chronic disease management programs.
- Patient engagement tools powered by AI saw a 20–25% boost in follow-up compliance and appointment retention.
- AI‑assisted EHR workflows have been shown to improve clinician satisfaction scores by 30%, which ties to retention and cost savings.
Consumer Trust and Demographics
- More than 1 in 3 Americans (35%) now use AI for health and wellness tasks, such as researching symptoms (31%), meal planning (25%), and emotional support (20%).
- 63% of users trust AI-generated health information more than social media (43%), though doctors still rank highest (93%).
- 75% of consumers expect disclosure when AI is used in healthcare communications, especially in clinical documentation or messaging.
- 72% of health system leaders cite improving consumer experience, engagement, and trust as a top 2025 priority.
- In countries like India and China, both patients and providers show higher readiness to use AI in direct care.
- Around 50% of global respondents are willing to share personal health data in return for personalized care.
- Barriers persist due to digital literacy gaps and inequities in internet access, particularly in marginalized groups.
Physician Readiness to Use AI in Clinical Practice
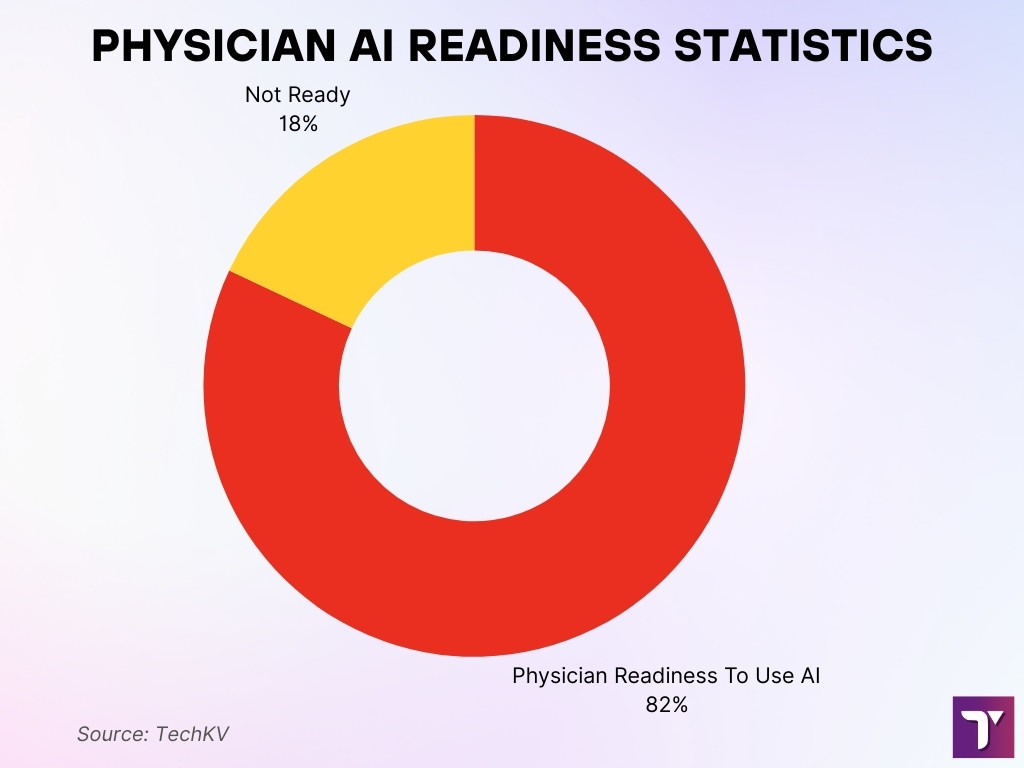
- 82% of physicians are either already using or are ready to use AI tools in clinical workflows.
- This figure reflects a growing confidence among healthcare providers in AI-assisted diagnostics, decision-making, and patient care support.
- The high adoption readiness indicates an accelerating shift toward technology-driven healthcare delivery.
- Visual representation shows a nearly full adoption circle, reinforcing strong acceptance of AI among medical professionals.
Challenges and Barriers to AI Adoption
- Key adoption barriers include financial constraints, regulatory ambiguity, low clinician uptake, technical gaps, and immature tools.
- Ethical concerns revolve around privacy, liability, data quality, interoperability, and professional accountability.
- Bias and poor data quality pose ongoing threats to clinical AI reliability and trust.
- Cybersecurity threats are rising, with insider threats now seen as more dangerous than external ones by 64% of healthcare firms.
- Only 44% of organizations use advanced behavioral analytics to catch these insider risks.
- 91% cite outdated systems, 91% worry about data privacy, and 58% list cyber threats as top AI barriers.
- 75% of providers say they lack adequate staff with strong generative AI skills.
Data Security and Privacy in AI Healthcare
- In 2024, 276.8 million healthcare records were breached, averaging 758,288 records per day, a 26% YoY increase.
- AI-related security incidents rose 56.4% in one year, with 233 reported cases in 2024.
- As of 2025, 36% of global data is health-related, yet 90% of that remains unstructured, complicating AI usage.
- Top risks include privacy, data governance, liability, bias, and resource drain from carbon costs.
- Differing regulations across GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA challenge cross-border deployments.
- With AI enabling faster data mining, gaps in consent management and real-time monitoring need urgent attention.
Emerging Technologies & AI Agents in Healthcare
- 80% of organizations use AI agents, 96% plan to expand, and 43% allocate over half of their AI budget to agentic AI.
- Use cases include clinical trial matching, medication reminders, and post-discharge support.
- AI voice agents like “Eva” replace the workload of 100 full-time employees, increasing efficiency fourfold.
- Emotion-aware AI companions reduce loneliness among older people, especially those with dementia or Alzheimer’s.
- Agentic assistants now help physicians code clinical notes or automate prior authorizations.
- Smart implants and connected biosensors provide at-home diagnostics with clinical-grade precision.
- AI avatars offer 24/7 support to patients with mental health needs or mobility challenges.
Conclusion
AI in healthcare has evolved from an experimental novelty to a powerful force reshaping every facet, from diagnostics and drug discovery to patient support, workflow automation, and agentic intelligence. While adoption accelerates, trust, data security, regulatory clarity, and workforce readiness will dictate the sustainability of this shift. The insights here paint a landscape rich with potential, but also rooted in responsibility.
The journey ahead demands balanced integration that augments human expertise, preserves clinician skills, and protects patient data. Healthcare leaders and policymakers must continue to guide AI with ethical frameworks, robust governance, and inclusive design to ensure that the technology uplifts rather than disrupts.
AI’s promise in healthcare is immense, but success lies not in technological capability alone, but in how we choose to deploy it for equitable, trusted, and effective patient care.
