Artificial intelligence continues to reshape global industries, and Large Language Models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT, Claude, Llama, and Gemini are now transforming how companies operate. By 2026, AI is no longer treated as an experimental advantage but a foundational capability that determines competitive survival. From customer service automation to document processing, from business intelligence to creative generation, LLMs are embedded into workflows everywhere.
Yet while interest in LLM adoption is increasing, one critical question remains widely misunderstood: What does it really cost to integrate ChatGPT and other LLMs?
Many companies begin this journey assuming LLM integration is simply a matter of connecting to an API. In reality, the financial considerations are far more complex. Integration costs extend into API usage, development, data engineering, compliance, infrastructure, monitoring, and long-term optimization. Without understanding the full cost structure, organizations risk underbudgeting, mismanaging resources, or being surprised by recurring expenses months after deployment.
The Rising Demand for LLM Integration
Before examining cost components, it is important to understand why LLM integration has become a strategic priority worldwide.
Businesses today operate under increasing pressure to modernize and automate. According to Statista, the global AI software market is projected to surpass US 200 billion by 2025, with significant growth continuing throughout 2026 and beyond. This forecast highlights AI as a central pillar of digital infrastructure:
LLMs like ChatGPT have evolved significantly. New capabilities such as extended context windows, advanced reasoning, faster inference speeds, enterprise-level governance, and improved versatility have made them suitable for mission-critical use cases. Companies now rely on LLMs for internal assistants, customer-facing chatbots, workflow automation, document summarization, multilingual communication, and knowledge retrieval.
As nearly every industry adopts AI-driven solutions, understanding the true cost of AI integration has become essential for long-term planning and sustainable deployment.
Understanding the Full Spectrum of LLM Integration Costs
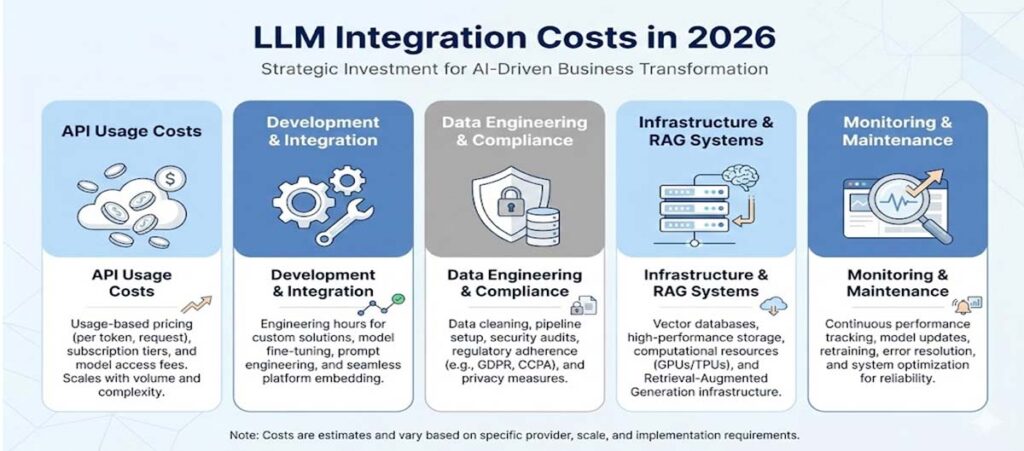
1. API Usage and Licensing Costs
The most visible cost associated with ChatGPT and other LLMs is token-based pricing. Businesses pay for both the input tokens they send and the output tokens the model returns. In 2026, API pricing varies widely depending on model version, performance tier, and usage volume.
Premium models naturally cost more, but they also generate longer and more detailed responses. Many companies underestimate token consumption because LLM output varies depending on prompt design, user behavior, and context size. This unpredictability makes accurate budgeting difficult, especially once usage increases across departments or customer interactions.
Enterprise licensing adds additional layers such as analytics dashboards, dedicated capacity, enhanced governance, and security isolation. Over time, these charges can become significant recurring expenses if not actively monitored.
2. Custom Development and System Integration Costs
Connecting an LLM to an existing system requires multiple layers of engineering, design, optimization, and testing. Many organizations must build custom interfaces, orchestrators, context managers, workflow engines, and response validation mechanisms. A customer support integration may require automated ticket handling, escalation logic, dynamic knowledge retrieval, and user feedback loops.
Meanwhile, an internal AI assistant for employees may involve access to internal documents, permission controls, and multi-turn reasoning capabilities. Development teams also handle error management, prompt optimization, latency tuning, rate-limit management, and user interface adjustments. The complexity increases further for companies that develop AI capabilities across several departments or products.
Enterprise-scale integrations often cost between US 80,000 and US 400,000, especially when multiple workflows, dashboards, and data sources must be connected. More advanced use cases such as autonomous agents, multimodal AI tools, or industry-specific decision systems require even larger investments.
3. Data Engineering, Security, and Compliance Costs
One of the most underestimated cost categories in LLM adoption involves preparing, securing, and governing the data that fuels the system. LLMs only deliver high-quality results when given structured, accurate, and relevant internal data.
Data engineering tasks often include extracting historical documents, cleaning and structuring text, labeling files, creating metadata, building embeddings, storing vectors, and creating retrieval systems. Companies with large or complex data ecosystems may spend months preparing their data for use with an AI model.
In regulated industries, the cost rises sharply due to privacy laws. Companies must implement encryption, anonymization processes, role-based access controls, audit logs, and compliance workflows. Legal and security teams frequently participate in the integration, adding both time and cost.
Wikipedia provides helpful context on the privacy, accuracy, and governance risks associated with LLMs:
Organizations with international operations may also face data residency requirements that restrict what information can leave a region. Meeting these requirements often demands custom infrastructure and increases integration cost.
4. Infrastructure, RAG Systems, and Hybrid Architectures
Modern AI deployments increasingly rely on Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG), where LLMs consult an internal knowledge base before generating answers. RAG dramatically improves accuracy but introduces new infrastructure components such as vector databases, embeddings stores, indexing systems, caching layers, and retrieval pipelines.
These infrastructure layers require their own hosting, scaling, and monitoring solutions. Cloud pricing varies depending on throughput, storage, and performance requirements. For large deployments, the infrastructure cost may exceed API usage costs.
Some companies reduce costs through hybrid model architectures, where smaller or open-source models handle routine tasks while high-end LLMs are reserved for complex reasoning. This approach provides long-term cost control but increases engineering and maintenance work upfront.
5. Monitoring, Maintenance, and Continuous Improvement Costs
Even after deployment, LLM systems require constant monitoring. AI models evolve quickly, pricing structures change, and new tools or capabilities are introduced regularly. To maintain consistent quality, organizations must continuously refine prompts, update connectors, test new model versions, evaluate performance, adjust workflows, and monitor cost spikes.
Without ongoing maintenance, AI performance gradually deteriorates. Errors become more frequent, latency increases, and token usage becomes inefficient. Annual maintenance can easily represent 20 to 40 percent of the original development cost.
In many cases, the long-term cost of keeping an AI system reliable exceeds the cost of building it, yet this fact rarely appears in online cost guides.
How Companies Can Reduce LLM Integration Costs
Organizations that plan strategically can significantly reduce both short-term and long-term costs. One of the most effective methods is to start with a single use case that offers clear and measurable ROI before expanding AI adoption across departments.
Companies can also save money by using smaller, specialized models for routine tasks and reserving advanced models for complex or high-value operations. Implementing semantic caching early is another proven strategy that reduces repetitive API calls and prevents token inflation.
Monitoring usage, setting alerts for cost spikes, auditing prompts regularly, and designing workflows with model efficiency in mind all contribute to better cost control. Planning for compliance and data governance from the beginning also prevents costly redesigns later.
A sustainable AI initiative requires continual improvements rather than a one-time setup. Organizations that budget for ongoing maintenance enjoy more consistent performance and better financial outcomes over time.
Final Thoughts: LLM Integration Requires Strategic Investment
Integrating ChatGPT or other LLMs into business systems provides remarkable potential for efficiency, innovation, and customer experience improvement. However, successful integration requires careful planning, realistic budgeting, and a thorough understanding of the long-term costs involved.
API pricing is only one part of the equation. The true cost of LLM integration includes development, data engineering, compliance, infrastructure, monitoring, governance, employee training, and ongoing optimization. Companies that recognize this full cost structure are better positioned to build sustainable AI systems that deliver measurable value.
LLMs represent one of the most transformative technologies of our time. The organizations that approach integration strategically, rather than impulsively, will be the ones that achieve the strongest competitive advantage in the years ahead.
