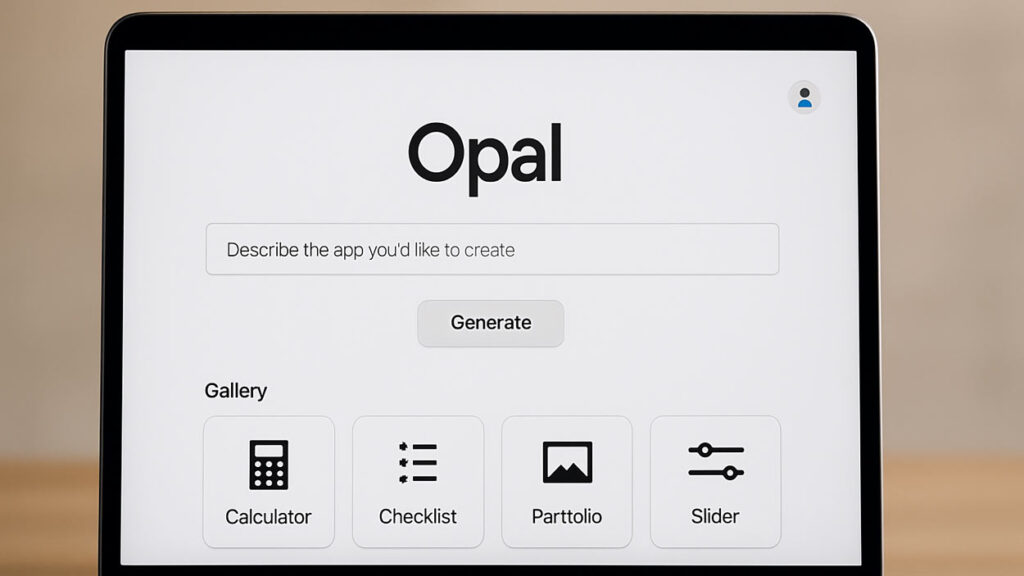
Opal is Google’s new AI tool that lets you build and share mini web apps just by describing them in plain language.
TLDR:
- Google is testing Opal, a no-code app builder powered by AI, under its experimental platform Google Labs.
- Users describe an app in text, and Opal generates a working prototype with visual workflow editing.
- Apps can be shared online, but the tool currently supports only front-end logic with limited backend capabilities.
- Part of a growing “vibe-coding” trend, Opal targets creatives and non-coders wanting to build apps without programming.
What Happened
Google quietly rolled out a new experimental app builder called Opal, aimed at making it easier for anyone to create simple web applications. Available through Google Labs in the United States, Opal leverages AI to turn plain English prompts into functional mini apps, complete with visual editing tools.
This move places Google alongside startups like Lovable and Cursor, and tech giants such as Canva, Figma, and Replit, all chasing the rapidly growing market for no-code tools powered by AI.
Opal Lets You Build Apps Without Writing Code
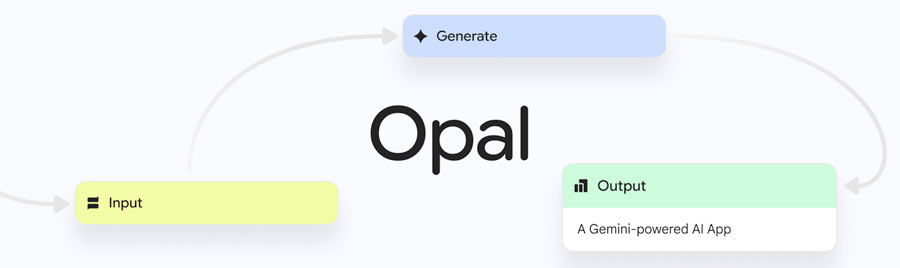
At its core, Opal is designed to simplify app creation by removing the need for traditional coding. Instead of writing lines of code, users describe the app they want to build in plain language. Google’s AI models interpret that input and generate a working prototype.
Once the app is created, users are guided into a visual workflow editor, where each step of the app process (input, logic, and output) is represented graphically. These steps can be clicked on and edited, allowing for customization of app logic or visuals. Users can also add new steps using a drag-and-drop toolbar.
From AI Studio to Opal: Expanding Google’s App-Building Vision
Google already offers developers tools like AI Studio to build apps using prompts, but Opal takes this vision further by making the process visual and accessible to non-developers. The goal is to help anyone from product thinkers to hobbyists bring their ideas to life.
Key features of Opal include:
- Text-to-app creation using Google’s language models
- Remixable gallery of public apps for inspiration
- Visual editing panel with customizable logic steps
- Web publishing and shareable links for user testing
- Basic access control requiring users to log in with a Google account
Opal Joins the “Vibe-Coding” Movement
The idea behind “vibe-coding” is shifting focus from technical implementation to creative intent. Users describe the vibe of what they want, like a checklist, calculator, or interactive portfolio and let AI handle the build. This trend is rapidly catching on, especially in design-forward and collaborative spaces.
Other platforms like Webflow, Bubble, and Glide have similarly empowered users to launch apps without deep technical skills. Analysts expect the no-code/low-code market to grow over 20 percent annually, according to a Gartner report, and Google clearly wants in.
Limitations and Future Potential
Early feedback highlights both promise and limitations. While Opal excels at building static front-end apps, it currently lacks:
- Backend integration
- Real-time data handling
- Advanced user authentication
Despite these gaps, Google may eventually integrate Opal into its broader ecosystem, possibly combining it with Firebase, Cloud Functions, or Google Workspace. For now, it remains an experimental tool inside Google Labs, open only to U.S. users.
What TechKV Thinks
I think Opal could be a game-changer for creators who want to test ideas quickly without getting bogged down in code. This tool makes app creation feel less intimidating and more fun. Sure, it’s not ready for full-scale apps yet, but for prototypes, portfolios, or side projects, Opal seems incredibly promising.
Google entering this space also tells us how serious the no-code movement has become. If Opal continues to evolve, it could become a core offering for anyone building digital tools even if they’ve never written a line of code.